机器学习和数学分析作业¶
SkyForm AIP提供了一些作业定义的例子和深度学习样板数据。这些材料在软件包 https://skyformaip.com/aip/skyformaip_examples.tar.gz里。
分布式TensorFlow的作业定义¶
TensorFlow 2.x 是一个与 TensorFlow 1.x 使用体验完全不同的框架,TensorFlow 2.x 不兼容 TensorFlow 1.x 的代码。SkyForm AIP同时支持TensorFlow 2.x和TensorFlow 1.x分布式作业。
分布式TensorFlow1.x的作业定义¶
分布式TensorFlow是由多个任务组成的。任务有Master,Parameter Server(ps)和Worker三类。在有GPU的情况下,Master和Worker利用GPU可以提高性能。
下面是TensorFlow学习mnist的作业定义例子:
{
# Mandatory.
# Job type for tensorflow job
"JobType": "tensorflow",
# Mandatory if task level command is not specified.
# Tensorflow job command
# The job level command will be inherited by each task if the task does
# not specify a command. Otherwise, task level command will overwrite
# job level command
"Command":"python mnist/model.py",
# Optional.
# A list of environment variables for the tensorflow job.
# The environment variables will be set for each task.
"Envs":
[
"TF_DATA_DIR=mnist/data",
"TF_MODEL_DIR=mnist/model",
"TF_TRAIN_STEPS=2000"
],
# Optional.
# The shared directory where the output of tasks will be written to.
# Each task will have a separate output file generated under:
# <TaskLogDir>/<JobID>.<User>/<Component>.<Index>.<Host>.<PID>
"TaskLogDir": "log",
# Optional.
# Suppress standard output and error of tasks. If TaskLogDir is specified,
# the standard output and error of tasks will still be written to the
# directory
"SuppressTaskOutput": false,
# Optional.
# Buffer standard output and error of tasks every second before printing
# out by task for better readability.
# If SuppressTaskOutput is set to true, this field is ignored.
"BufferTaskOutput": false,
# A list of task specification
"Tasks":
[
{
# Mandatory.
# Component name for the task
"Component":"PS",
"MinNumTasks": 1,
"MaxNumTasks": 2,
"Resource":
{
# 若系统中主机没有定义ps标签,删除以下这行。可用chinfo查看主机标签
"Select": "ps"
}
},
{
"Component":"MASTER",
"MaxNumTasks": 1,
"Resource":
{
"Need": "gpu=2"
}
},
{
"Component":"WORKER",
"MinNumTasks": 2,
"MaxNumTasks": 4,
"Resource":
{
"Need": "gpu=1"
}
}
]
}
参数说明:
- JobType:
必须定义为tensorflow,以便于作业控制器针对TensorFlow的任务做合理的处理,如为每个任务设置端口。
- Command:
定义运行Python的程序
- Envs:
定义TensorFlow所需的环境变量:TF_DATA_DIR,TF_MODEL_DIR,和TF_TRAIN_STEPS。 请参考TensorFlow的说明设置这些变量。
- TaskLogDir:
定义一个目录放置各个任务的输出。每个任务的输出会写到单独的一个文件里,以便观察和排错。 若不定义该目录,各个任务的输出会显示在命令aip job run的终端上,各个任务的输出的每行的 前段会增加一个判别该任务的字串,以方便识别。因为各个任务是并行执行的,各个任务的输出行会交替。
- SuppressTaskOutput:
禁止任务输出到终端上,以便排错。一般不需要修改该参数。
- BufferTaskOutput:
为了方便观察各任务交替输出的结果,这个参数设成true时各个任务的输出会在各自的缓冲区里,每秒集中输出一次, 这样每个任务在每秒内的输出集中显示到终端上,方便观察。
- Tasks: 定义各类任务数和所需资源。
- Component:
任务类别名,值必须是MASTER、PS、或WORKER。
- MinNumTasks/MaxNumTasks:
此类任务的最小和最大任务数。在集群的环境中,任务多的作业不容易有机会拿到大块资源而长期等待。 而任务数若定义少了又会减少并行度,影响作业运行时间。定义最小和最大任务数可以让调度器根据最大任务数调度资源,当资源不能满足最大任务数是,减少任务数目,直到最小值为止,这样能让作业的等待时间缩短并最大可能地得到可用资源。
当MinNumTasks没有定义时,默认为1。当MaxNumTasks没有定义时,默认于MinNumTasks相等。
- Resource:
定义每个任务所需的资源。以上的例子中,MASTER任务只有一个,需要两个GPU, 而每个WORKER需要1个GPU。
运行作业:
aip job run tensorflow.mnist.json
当作业开始运行时,作业控制器会:
根据调度器分配的主机槽位启动任务
根据调度器分配的各主机上的端口为TensorFlow任务设置所用端口
根据调度器分配的各主机上的GPU为每个需要GPU的任务设环境变量CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES控制任务可用的GPU。
监控各个任务状态和资源使用(CPU和内存)情况。
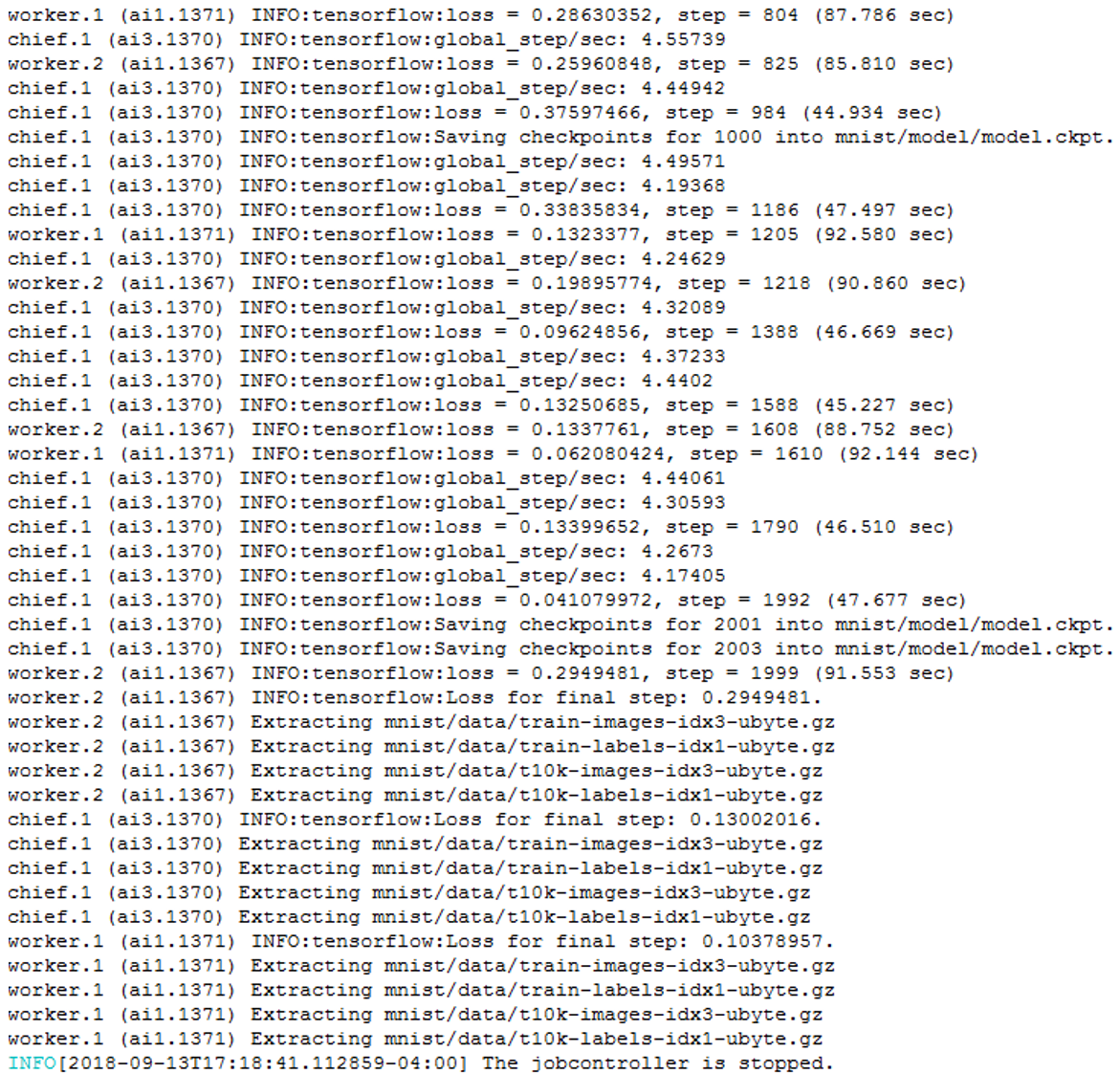
除了作业的终端输出外,我们可以在另一个终端里看到各个任务的输出内容:
作业屏幕输出例子:
分布式TensorFlow2.x的作业定义¶
Tensorflow2.x提供分布式策略接口,用户只需要改动较少代码就能分布现有模型和训练代码, 让单机运行的训练任务在多个GPU、多台机器上进行分布式训练。
分布式TensorFlow2.x是由多个任务组成的,所有的任务都是Worker。其中,第一个Worker是“主要”工作者, 除了常规的训练工作之外,还承担了更多的责任,比如保存检查点和为TensorBoard编写摘要文件。 在有GPU的情况下,Worker利用GPU可以提高性能。
多机分布式TensorFlow2.x作业使用csub命令提交,使用tf-run.sh命令运行, 同时支持GPU或者CPU运行训练任务。
下面是TensorFlow2.x学习mnist的作业定义例子:
csub -n 4,8 -R "span[ptile=2] rusage[gpu=1]" -o %J.out -e %J.err tf-run.sh multi.py
参数说明:
- -n:
需要的最小和最大worker数。比如例子中“4,8”,最少需要4个worker,最多需要8个worker。 当最小worker数都不满足时,作业处于pending状态,等待空闲资源;如果最小worker数满足, 训练任务开始执行;如果集群有更多空闲资源,调度器会尽可能多的启动worker, 同时不超过设定的最大worker数。如果只指定最小worker数,不指定最大worker数,比如“-n 4”, 指定worker数为4,即不使用弹性资源分配。
- -R:
定义作业运行的资源需求。比如例子中“span[ptile=2]”,要求每个节点启动两个 worker;“rusage[gpu=1]”,要求给每个worker分配一块GPU。“-R”支持更多的资源需求表达式, 具体用法请参考 csub 里-R的说明。
- -o:
定义标准输出写入文件的路径。%J指定文件名为作业号。
- -e:
定义标准错误输出写入文件的路径。%J指定文件名为作业号。
- tf-run.sh:
AIP 例子 里tensorflow2目录下 提供的TensorFlow2.x多机分布式训练任务的wrapper, 负责将训练任务在调度器分配的资源上启动,并监控训练任务状态和收集资源使用信息。 TensorFlow2.x多机分布式训练任务必须通过tf-run.sh启动。
- multi.py:
运行训练任务的Python程序,后面可以跟程序参数,程序名和参数都是用户自定义的,比如“main.py –epoch=10”。
csub命令支持更多参数,具体用法请参考 csub 。
当提交作业并开始运行时,tf-run.sh会:
根据调度器分配的主机槽位启动任务
根据调度器分配的各主机上的端口为TensorFlow任务设置所用端口
根据调度器分配的各主机上的GPU为每个需要GPU的任务设环境变量CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES控制任务可用的GPU。
监控各个任务状态和资源使用(CPU和内存)情况。
以下功能是训练任务程序自己实现的,tf-run.sh不会涉及,SkyForm AIP只提供基于分布式文件系统的共享目录:
在分布式文件系统中保存检查点文件,以便在重新启动先前失败的实例后,将获得以前的状态,继续训练。
为可视化工具TensorBoard编写摘要文件,包含模型,数据和graph等信息。
Epoch、batch_size、learning_rate等跟训练相关的参数。
下载训练数据和保存模型等跟训练相关的功能。
TensorBoard是一套Web应用程序,用于检查和了解模型运行和图形。 TensorBoard当前支持五种可视化: 标量,图像,音频,直方图和图形 。通过TensorBoard可以监控训练的收敛性, 方便调整参数epoch、batch_size、learning_rate等。
可以通过AIP启动TensorBoard:
csub tbjob logs
Job 7455 has been submitted to the default queue [medium].
cread 7455
Messages posted to jobID 7455
POST_TIME: May 2 22:17:47 MESSAGE: /ajj/192.168.10.100/16332/18e19598ce5aa95108fd30a9630e93e9
把上面的MESSAGE里的URL拷贝到AIP门户的主机URL后,如:
https://10.1.22.3/ajj/192.168.10.100/16332/18e19598ce5aa95108fd30a9630e93e9
以上的例子中,AIP门户安装在10.1.22.3上。
分布式MXNet的作业定义¶
类似于TensorFlow,分布式MXNet的任务分成scheduler、server、和worker。 下面是一个包含1个scheduler,2个server和2个worker的例子:
{
# Mandatory.
# Job type for mxnet job
"JobType": "mxnet",
"Interactive": false,
# Mandatory if task level command is not specified.
# Mxnet job command
# The job level command will be inherited by each task if the task does
# not specify a command. Otherwise, task level command will overwrite
# job level command
"Command":"python image_classification.py --dataset cifar10 --model vgg11 --epochs 1 --kvstore dist_sync",
# Optional.
# A list of environment variables for the mxnet job.
# The environment variables will be set for each task.
# Specify NIC for mxnet communication if machines have multiple NICs
# "Envs": ["DMLC_INTERFACE=enp0s8"],
# Optional.
# The shared directory where the output of tasks will be written to.
# Each task will have a separate output file generated under:
# <TaskLogDir>/<JobID>.<User>/<Component>.<Index>.<Host>.<PID>
"TaskLogDir": "log",
# Optional.
# Suppress standard output and error of tasks. If TaskLogDir is specified,
# the standard output and error of tasks will still be written to the
# directory
"SuppressTaskOutput": false,
# Optional.
# Buffer standard output and error of tasks every second before printing
# out by task for better readability.
# If SuppressTaskOutput is set to true, this field is ignored.
"BufferTaskOutput": false,
# A list of task specification
"Tasks":
[
{
# Mandatory.
# Component name for the task
"Component":"scheduler",
"MaxNumTasks": 1
},
{
"Component":"server",
"MaxNumTasks": 2
},
{
"Component":"worker",
"MaxNumTasks": 2
}
]
}
我们加了一个参数“Interactive”: false让作业在后台运行。
aip job run mxnet.json
分布式PyTorch的作业定义¶
PyTorch有master和worker两类任务,一般master是一个任务,worker则有多个。以下是PyTorch的作业定义:
{
# Mandatory.
# Job type for pytorch job
"JobType": "pytorch",
# Mandatory if task level command is not specified.
# Pytorch job command
# The job level command will be inherited by each task if the task does
# not specify a command. Otherwise, task level command will overwrite
# job level command
"Command":"python main.py --epochs=3",
# Optional.
# A list of environment variables for the pytorch job.
# The environment variables will be set for each task.
"Envs": [],
# Optional.
# The shared directory where the output of tasks will be written to.
# Each task will have a separate output file generated under:
# <TaskLogDir>/<JobID>.<User>/<Component>.<Index>.<Host>.<PID>
"TaskLogDir": "",
# Optional.
# Suppress standard output and error of tasks. If TaskLogDir is specified,
# the standard output and error of tasks will still be written to the
# directory
"SuppressTaskOutput": false,
# Optional.
# Buffer standard output and error of tasks every second before printing
# out by task for better readability.
# If SuppressTaskOutput is set to true, this field is ignored.
"BufferTaskOutput": false,
# A list of task specification
"Tasks":
[
{
# Mandatory.
# Component name for the task
"Component":"master",
"MaxNumTasks": 1
},
{
"Component":"worker",
"MinNumTasks": 3
}
]
}
然后用命令提交作业:
aip job run pytorch.json
TensorBoard已经集成到PyTorch项目中,PyTorch也可以使用TensorBoard的可视化功能。 PyTorch程序负责保存摘要文件,比如保存到目录runs,启动TensorBoard检查PyTorch运行情况的方法与 TensorFlow2.x的例子相同:
csub tbjob runs
Intel Caffe MPI作业¶
Intel Caffe是利用Intel MPI(Message Passing Interface)并行框架的Caffe分支。 其作业定义较为简单,如以下例子:
{
"Command": "mpirun build/tools/caffe train --solver=cifar10/cifar10_full_solver.prototxt", # Mandatory. Command to run.
"MinNumSlots": 2, # Minimum replicas of the job to run.
# Defaults to 1.
"MaxNumSlots": 4, # Maximum replicas of the job to run.
}
在这个例子中,我们定义最小任务数为2,最大任务数为4。调度器至少调度最小任务数,并会最大可能满足最大任务数。
作业运行用命令:
aip job run caffe.json
分布式Ray作业定义¶
Ray是一个针对强化学习以及类似学习过程而设计的一个分布式计算框架,囊括强化学习主要计算并分布式化, 包含模型训练,模型推理和仿真。Ray并不替代深度学习框架,而是叠合使用、无缝集成, 即同样的强化学习算法既可以使用TensorFlow的框架,也可以使用PyTorch的框架。
Ray的优势之一就是能够将一个程序运行在多机器集群中,集群由一个head节点和多个worker节点组成。 Head节点需要先启动,然后worker节点使用head节点的地址启动以形成集群。在有GPU的情况下, worker节点利用GPU可以提高性能。
SkyForm AIP可以为Ray程序构建满足资源需求的集群,启动程序运行在集群上,并在任务结束后自动销毁集群。
利用 AIP 例子 里ray目录下的ray-run.sh脚本, 以下是Ray利用PyTorch框架学习mnist的作业定义例子:
csub -R "2 {span[hosts=1]} 4 {span[ptile=2] rusage[gpu=1]}" -I ray-run.sh train_fashion_mnist_torch.py
参数说明:
- -R:
定义作业运行的资源需求。Ray作业包含head节点和worker节点,节点数量和资源需求都不同,需要使用SkyForm AIP多节资源需求。
多节资源需求的语法为:n1{资源需求} n2{资源需求}…
其中n1,n2为CPU核数。比如例子中“2 {span[hosts=1]} 4 {span[ptile=2] rusage[gpu=1]}”,表示head节点需要2个核,分布在一台机器上;worker节点需要4个核, 每个节点两个核,同时每个核对应一块GPU。
- -I:
交互式作业。作业标准输出重定向到终端,可选。也可以通过-o将作业标准输出重定向到文件中。
- ray-run.sh:
SkyForm AIP提供的Ray多机分布式计算的wrapper,负责将head节点和worker 节点在调度器分配的资源上启动,启动Ray程序,并监控任务状态和收集资源使用信息。 当Ray程序运行结束后,销毁Ray集群。Ray多机分布式计算任务必须通过ray-run.sh启动。 ray-run.sh根据调度器分配的机器和端口,在启动Ray程序前会设置环境变量“ip_head”, 供Ray程序初始化时使用,比如:ray.init(address=os.environ[“ip_head”])
- Train_fashion_mnist_torch.py:
Ray的Python程序,后面可以跟程序参数,程序名和参数都是用户自定义的。
作业屏幕输出例子:
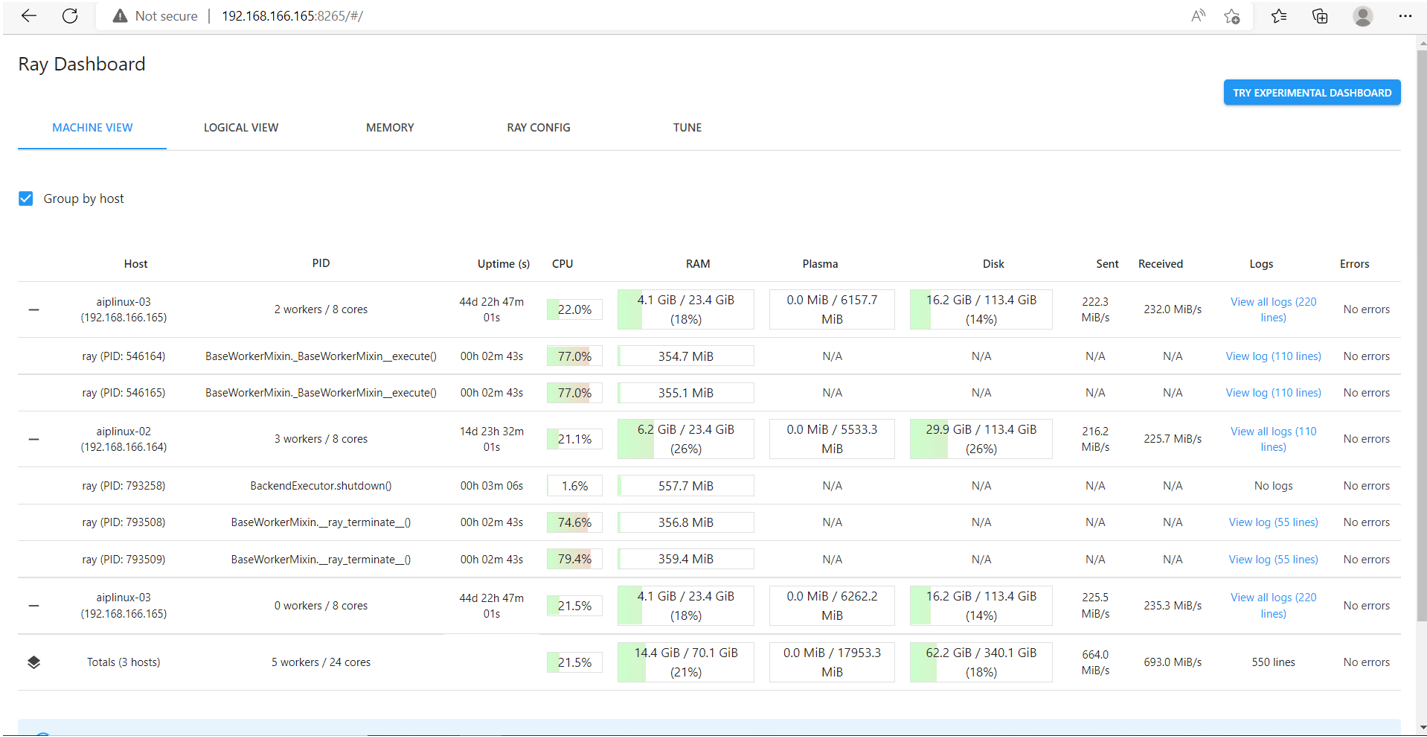
Ray提供内置的dashboard,启动在head节点,默认端口8265。
访问dashboard:http://192.168.166.165:8265
Spark集群作业¶
Apache Spark是高速通用集群计算框架,广泛应用与大数据分析等领域。SkyForm AIP可以根据用户的要求动态为作业生成一个Spark集群。作业结束时Spark集群则自行消失而释放资源。
准备Scala应用例子。使用工具sbt来创建应用:
curl https://bintray.com/sbt/rpm/rpm | \
tee /etc/yum.repos.d/bintray-sbt-rpm.repo
yum install sbt
准备应用JAR包:
sbt package
...
[info] Packaging {..}/{..}/target/scala-2.12/simple-project_2.12-1.0.jar
准备作业定义。以下例子里用一个master和2各Slave。其中
环境变量SPARK_HOME必须设。
最后的一个Component为客户程序。
{
# Mandatory.
# Job type for Spark job
"JobType": "spark",
# Mandatory.
# A list of environment variables for the Spark job.
# The environment variables will be set for each task.
# The environment SPARK_HOME is mandatory.
"Envs": ["SPARK_HOME=/opt/skyformai_shared/spark"],
# Optional.
# The shared directory where the output of tasks will be written to.
# Each task will have a separate output file generated under:
# <TaskLogDir>/<JobID>.<User>/<Component>.<Index>.<Host>.<PID>
"TaskLogDir": "",
# Optional.
# Suppress standard output and error of tasks. If TaskLogDir is specified,
# the standard output and error of tasks will still be written to the
# directory
"SuppressTaskOutput": false,
# Optional.
# Buffer standard output and error of tasks every second before printing
# out by task for better readability.
# If SuppressTaskOutput is set to true, this field is ignored.
"BufferTaskOutput": false,
# A list of task specification
"Tasks":
[
{
# Mandatory.
# Component name for the task
"Component":"master",
"Command":"sparkcluster",
"MaxNumTasks": 1
},
{
# Mandatory.
"Component":"worker",
"Command":"sparkcluster",
"MinNumTasks": 2
},
{
# Mandatory.
"Component":"client",
"Command":"spark-submit --class SimpleApp target/scala-2.12/simple-project_2.12-1.0.jar spark.json",
"MaxNumTasks": 1
}
]
}
提交作业:
aip job run spark.json
若是单机Spark应用,则可用简单的作业定义:
{"Command": "/opt/skyformai_shared/spark/bin/spark-submit --class SimpleApp target/scala-2.12/simple-project_2.12-1.0.jar spark.json"}
Megatron-deepspeed¶
微软通过将其 DeepSpeed 库集成到 NVIDIA 的 Megatron-LM 框架中,开发出了 Megatron-DeepSpeed。
DeepSpeed 是微软的优化库,旨在简化和增强分布式训练和推理。DeepSpeed 引入了一系列优化措施, 简化了流程,使其更加高效。
Megatron-LM 是 NVIDIA 的大型强大转换器。它可以处理海量模型和复杂的深度学习任务, 是 DeepSpeed 带来进步的理想起点。
Megatron-DeepSpeed 的与众不同之处在于它全面支持一系列功能,从混合专家模型训练到课程学习。 这使得它成为应对深度学习领域各种挑战的多功能工具。
使用 Megatron-DeepSpeed,您可以以前所未有的效率和规模训练更大规模的模型。
以下的作业启动程序分两个部分:把AIP在多台主机上为作业分配的CPU、GPU、和端口转换成Megatron-DeepSpeed 需要的环境变量;利用AIP的远程任务启动程序启动分布式任务。
mtds.sh:
#!/bin/bash
# AIP为作业设置了环境变量CB_ALLOCATION,描述资源分配详情
# 1. 准备环境变量,这部分的代码对所有分布式训练的作业基本一致,有通用性
nodes_array=($(echo $CB_ALLOCATION|python -c 'import json, sys; parsed = json.load(sys.stdin); hosts = [d["Hosts"] for d in parsed]; print([dd["Name"] for dd in hosts[0]])'|sed "s/'//g;s/\[//g;s/\]//g;s/,//g"))
ports_array=($(echo $CB_ALLOCATION|python -c 'import json, sys; parsed = json.load(sys.stdin); hosts = [d["Hosts"] for d in parsed]; print([dd["Port"] for dd in hosts[0]])'|sed "s/'//g;s/\[//g;s/\]//g;s/,//g"))
nodes_array=($CB_MCPU_HOSTS)
slots=0
nnodes=0
nodes=""
for (( i=0; i<${#nodes_array[*]}; i++ ));
do
nodes=$nodes" "${nodes_array[$i]}
nnodes=$(($nnodes+1))
i=$((i+1))
slots=$(($slots+${nodes_array[$i]}))
done
nproc_per_node=$(($slots / $nnodes ))
# PROC_NODE_LIST: 分配的主机名阵列,例子:node2 node2 node1 node1
export PROC_NODE_LIST="${nodes_array[@]}"
# PROC_PORT_LIST: 分配的端口阵列,例子:16331 16332 16331 16332
export PROC_PORT_LIST="${ports_array[@]}"
# NPROC_PER_NODE: 每台主机上的任务数,例子:2
export NPROC_PER_NODE=$nproc_per_node
# NPROCS: 总任务数,例子:4
export NPROCS=$slots
# NODE_LIST: 主机列表,例子:node2 node1
export NODE_LIST=$nodes
# NUM_NODES: 总主机数
export NUM_NODES=$(echo $nodes | wc -w)
# 2. 启动任务
n=0
for host in $NODE_LIST; do
runtask -z $host torchrun \
--nproc_per_node=$NPROC_PER_NODE \
--nnodes=$NUM_NODES \
--node_rank=$n \
--master_addr=$PROC_NODE_LIST[0] \
--master_port=$PROC_PORT_LIST[0] \
$@ &
n=$((n+1))
done
wait
备注
AIP分配GPU后,根据环境变量GPU_ALLOCATION的值,在作业的第一台主机上自动设置环境变量 CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES,通过runtask启动任务时,runtask会解析GPU_ALLOCATION的内容,在 运行任务前,设置相应的CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES值。所以以上的作业启动器mtds.sh里没有处理 GPU分配的逻辑。
提交作业例子:
csub -n 4 -R "rusage[gpu=1] span[ptile=2]" -o %J.out ./mtds.sh pretrain_gpt.py \
--num-layers 24 --hidden-size 1024 \
--num-attention-heads 16 --micro-batch-size 8 --global-batch-size 64 \
--seq-length 1024 --max-position-embeddings 1024 --train-iters 500 \
--lr-decay-iters 320000 --save /ai/Megatron-DeepSpeed/checkpoints/gpt2 \
--load /ai/Megatron-DeepSpeed/checkpoints/gpt2 \
--data-path /ai/Megatron-DeepSpeed/data/meg-gpt2_text_document \
--vocab-file /ai/Megatron-DeepSpeed/data/gpt2-vocab.json \
--merge-file /ai/Megatron-DeepSpeed/data/gpt2-merges.txt \
--data-impl mmap --split 949,50,1 --distributed-backend nccl \
--lr 0.00015 --lr-decay-style cosine --min-lr 1.0e-5 \
--weight-decay 1e-2 --clip-grad 1.0 --lr-warmup-fraction .01 \
--checkpoint-activations --log-interval 100 --save-interval 100 \
--eval-interval 100 --eval-iters 10 --fp16
以上的例子的csub参数:
-n: 4个子任务
-R “rusage[gpu=1] span[ptile=2]”:每个任务1个GPU,每台主机2个任务
使用容器¶
如果使用容器跑例子中的作业,则需要定义容器镜像,以及docker run的命令参数,其他命令不变。例子:
# CB_TASK_DOCKER_IMAG 指向容器镜像名
export CB_TASK_DOCKER_IMAGE=megatron-deepspeed:pytorch2.0.1-cuda11.7-cudnn8
# CB_TASK_DOCKER_OPTIONS 定义挂载到容器里的目录和传进容器的环境变量
export CB_TASK_DOCKER_OPTIONS="-v /share/home/cadmin/ai:/ai
-e NCCL_SOCKET_IFNAME=enp1s0f0 -e GLOO_SOCKET_IFNAME=enp1s0f0
-w /ai/Megatron-DeepSpeed -e HOME=/tmp"
# 作业提交与裸金属一样
csub -n 4 -R "rusage[gpu=1] span[ptile=2]" -o %J.out ./mtds.sh pretrain_gpt.py \
--num-layers 24 --hidden-size 1024 \
--num-attention-heads 16 --micro-batch-size 8 --global-batch-size 64 \
--seq-length 1024 --max-position-embeddings 1024 --train-iters 500 \
--lr-decay-iters 320000 --save /ai/Megatron-DeepSpeed/checkpoints/gpt2 \
--load /ai/Megatron-DeepSpeed/checkpoints/gpt2 \
--data-path /ai/Megatron-DeepSpeed/data/meg-gpt2_text_document \
--vocab-file /ai/Megatron-DeepSpeed/data/gpt2-vocab.json \
--merge-file /ai/Megatron-DeepSpeed/data/gpt2-merges.txt \
--data-impl mmap --split 949,50,1 --distributed-backend nccl \
--lr 0.00015 --lr-decay-style cosine --min-lr 1.0e-5 \
--weight-decay 1e-2 --clip-grad 1.0 --lr-warmup-fraction .01 \
--checkpoint-activations --log-interval 100 --save-interval 100 \
--eval-interval 100 --eval-iters 10 --fp16